How to Fix Access, Login, and Redirect Issues
When restoring a site with Duplicator, you may encounter access issues such as login and redirect issues. These errors are usually related to web server configurations, plugin conflicts, or incorrect settings. This guide will help you troubleshoot and resolve these issues.
403 Access Denied
If you see a “403 Forbidden” or “403 Access Denied” error after installing your site, it means the web server is restricting access to a specific path. Duplicator does not control this, but you can try the following solutions:
Solution 1: Contact Your Host
If you’re not familiar with web server configurations, contact your hosting provider and provide them with the URL where the issue occurs. They can usually resolve this issue quickly.
Solution 2: Edit Web Server Configuration
If you have server access, edit the Apache configuration file (httpd.conf, or httpd-ssl.conf for SSL sites) and add:
# The Directory path below should match your server the following is a SAMPLE
<Directory /var/www/html/example.com/public_html>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
After making changes, restart Apache.
Solution 3: Additional Resources
For more details on resolving 403 errors, please see this guide: “How to Fix the 403 Forbidden Error in WordPress” by WPBeginner.
404 Errors & Redirect Issues
If your site shows a 404 error, redirects incorrectly, or prevents logging in, try these solutions:
Solution 1: Fix Redirect Issues
Redirects may come from the following issues. Check each item for the possible issue and the solution:
- Misconfigured files like
wp-config.php,.htaccess, or themefunctions.phpfiles.- Check the
.htaccessfile for unnecessary redirects. - Try to remove your
.htaccessfile and generate a new one in Settings » Permalinks in WordPress.
- Check the
- A redirect plugin.
- Disable plugins using the Installer.
- Server-side redirects.
- Check cPanel settings or ask your host.
- The WordPress permalinks are misconfigured.
- Follow these steps for troubleshooting WordPress permalinks.
- Check the
installer-log.txtfile for additional warnings or errors.
Solution 2: Fix Path Issues
If “index.php” appears in the address bar or attached to each HTTP request, you will need to update your Apache configuration.
To allow permalinks in Apache, you need to instruct Apache to allow individual sites to update the .htaccess file, by adding the following options to the Directory section in your hosts Apache httpd.conf configuration file:
Add the following to the httpd.conf file.
# The Directory path below should match your server the following is a SAMPLE
<Directory /var/www/html/example.com/public_html>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
Restart Apache afterward. If you’re on a budget host with no access to the httpd.conf file you will need to send this FAQ entry to your host.
Solution 3: Check Plugins & Themes
Redirect issues can often be caused by plugins or themes.
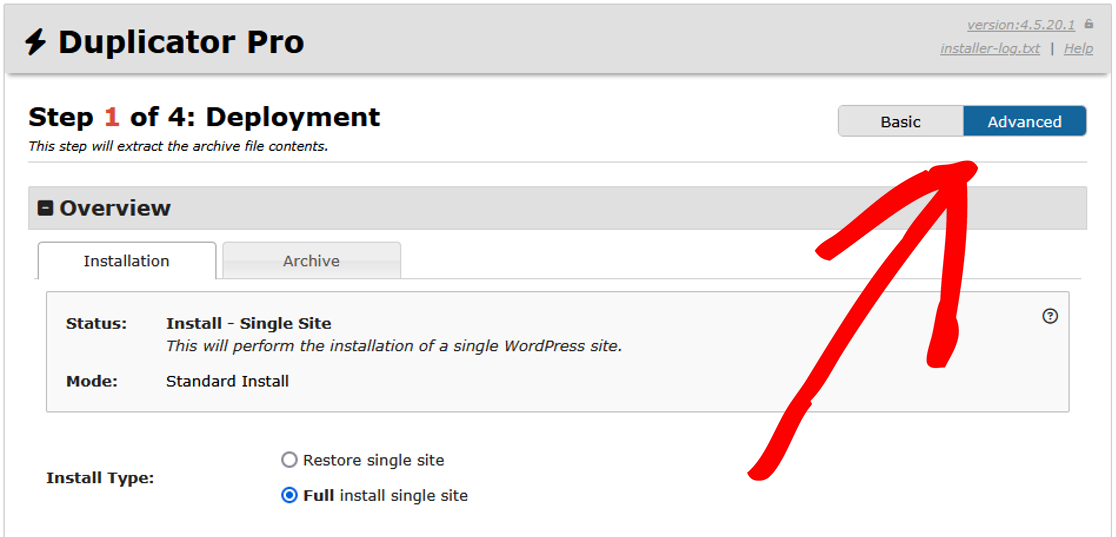
To quickly isolate common issues and disable plugins while running the Installer, start by enabling Advanced Mode in the upper-right-hand corner, and make sure that Full Install is selected if you choose to use Safe Mode.
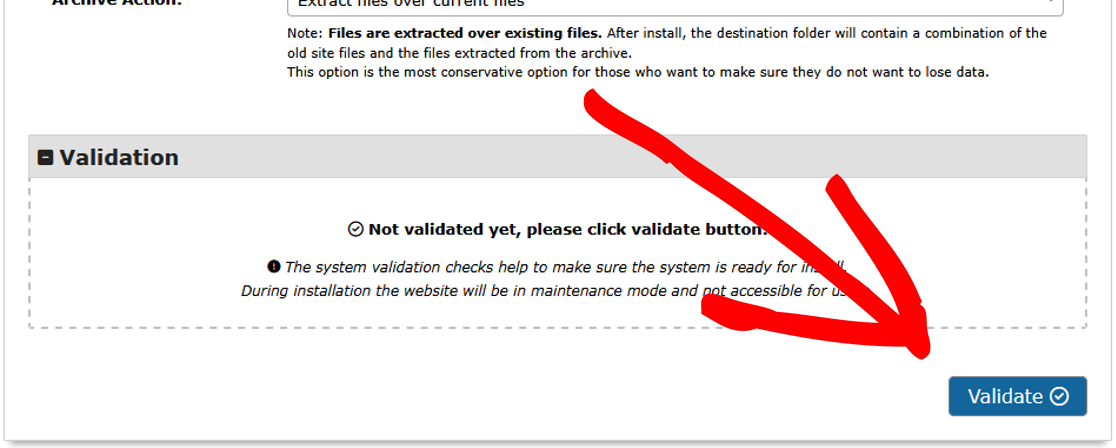
Next, enter the Database Connection information under Setup and then click Validate.
To disable all plugins at once:
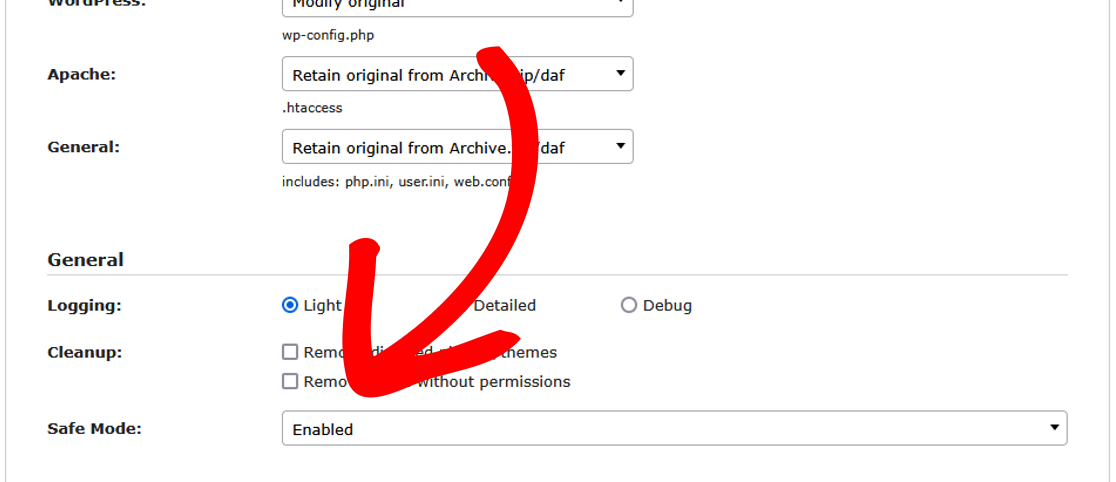
- When beginning Step 1 of the Installer, use Options » Advanced » Safe Mode.
- Set the dropdown to Enabled.
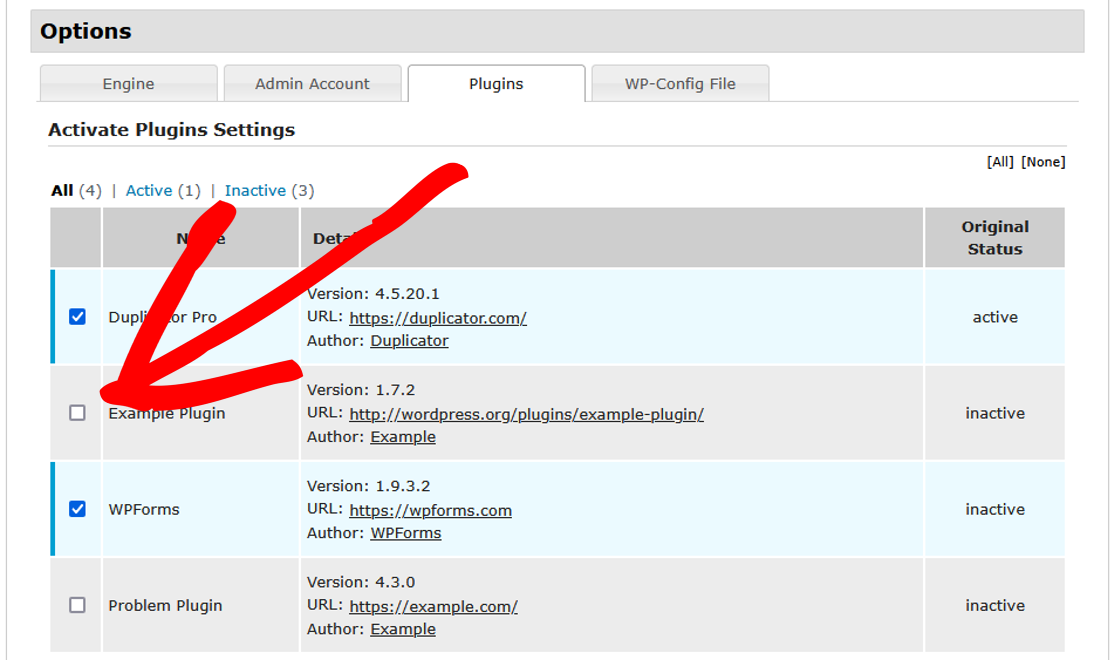
To disable only certain plugins plugins:
- When beginning Step 3 of the Installer, use Options » Active Plugins to disable individual plugins one-by-one by unchecking them.
It’s recommended to use Safe Mode first. If you suspect certain plugin(s) are causing the issue, disable Safe Mode and then disable those specific plugins in Step 3 as shown above. Finally, after logging into your WordPress admin, re-enable each plugin one by one, and resave any settings if applicable, until the problem is found.
If the issue still persists after trying the options above, consider investigating your theme’s functions.php to make sure there is no custom code causing a redirect. Also, consider looking at some of the solutions in this FAQ.
Solution 4: Clear the Browser Cache
Google Chrome and other browsers will cache your 301 redirects.
To clear the browser cache in multiple browsers, check out this guide. You should then be able to retest the site again. If you have just recently encountered the redirect, you likely only need to delete data from the past hour.
Alternatively, use an incognito/private browsing window. In that case, the cache is flushed after the browser is closed.
WordPress Admin Login Issues
If you cannot log in after installation, try these solutions:
Solution 1: Add a New Admin User
In the Duplicator Installer, make sure that Advanced Mode is enabled on the first screen.
Then, in Step 3, under Options » Create New User, make a new admin user.
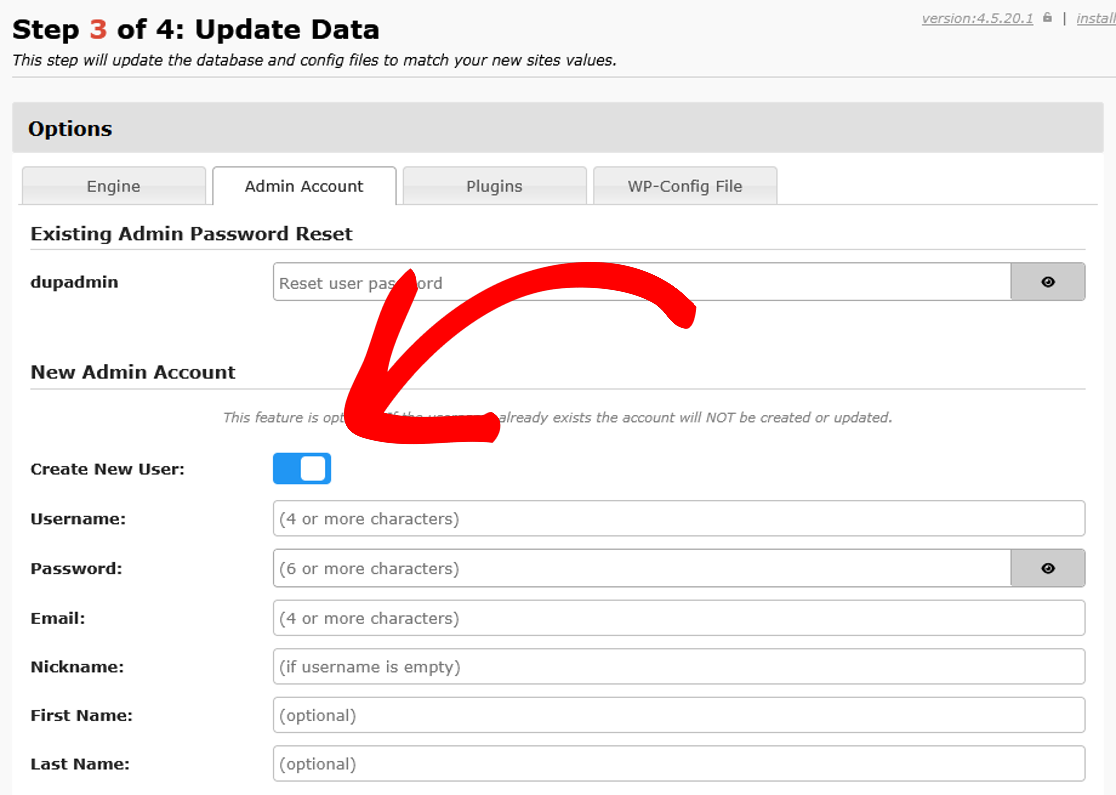
Use this new account to log in.
Solution 2: Validate or Reset Login
- Try resetting the password via the Lost your password? link on the login screen.
- Disable plugins during installation to rule out conflicts, using the steps here.
- You may have to reset the password by following these instructions.
- If all other options fail you can use the emergency password reset script.
Solution 3: Fix Redirect Issues
If you are trying to log in to the WordPress admin dashboard, but keep getting redirected back to the login without any notice of invalid username/password, then the login redirect might be messed up. Try changing the URL address in your browser to either of the following addresses and then try to login:
https://yoursite.com/wp-adminhttps://yoursite.com/wp-login.php
wp-config.php Errors
If errors appear after importing the site, they may be due to wp-config.php file misconfiguration. The plugin copies all defined constants from your wp-config.php file. However, due to the complexity of how these constants are initialized in PHP, there are rare cases where the replication of your previous wp-config.php may fail—either silently or with an error.
Some examples are:
- Backslashes or other custom settings.
- A defined constant is initialized with a flow check.
- Dynamic variables are concatenated to your plan value.
In such circumstances, you might see the following in the logs:
PHP ERROR: Unexpected end of file
PHP WARNING: Use of undefined constant
Solution 1: Inspect wp-config.php
- Open
wp-config.phpand check for missing constants or syntax errors. - Fix any broken values or incorrect paths.
- Check the macros for broken values in the case of complex initialization with flow checks, dynamic variables, backslashes, etc.
Solution 2: Reset wp-config.php
If errors persist, create a new wp-config.php manually:
- Download a fresh
wp-config.phpfrom WordPress.org. - Edit it with your database details.
- Replace your existing
wp-config.phpfile.
If the issue persists, reach out to your hosting provider.
That’s it! We hope this guide helped you any fix access, login, and redirect issues that you were facing.
If you are looking for a way to solve migration issues, check out our guide: “How to resolve WordPress migration issues?.”